🔧 TNV Working Priciple
The core working principle of the Direct-Fired Thermal Recovery Waste Gas Incinerator (TNV) is to directly introduce waste gas into the combustion chamber, where VOCs are incinerated and decomposed at high temperatures, and then the heat from the post-combustion flue gas is recovered through a heat exchanger, achieving a combination of waste gas purification and waste heat utilization. Its core difference from RTO lies in the absence of a heat storage medium, completing the treatment through 'direct firing + heat exchange', resulting in a simpler structure.
A. Core Working Principle (Four-Step Process)
The operating process of TNV revolves around two core links: 'incineration purification' and 'heat recovery', with clear and continuous steps:
1. **Waste Gas Pre-Treatment**:
The VOCs waste gas to be treated first passes through a filtration device (such as a dry filter) to remove impurities like paint mist and dust. This step prevents subsequent blockage or contamination of the combustion chamber and heat exchanger, ensuring stable equipment operation.
2. **High-Temperature Direct Combustion and Decomposition**:
After pre-treatment, the waste gas enters the combustion chamber, mixes with auxiliary fuel (such as natural gas), and is ignited for combustion. The combustion chamber temperature is maintained at 750~900°C. At this temperature, VOCs in the waste gas are thoroughly oxidized and decomposed into harmless CO₂ and H₂O, with a purification rate of over 99%.
3. **Waste Heat Recovery and Utilization**:
The high-temperature flue gas generated after combustion (approximately 700~850°C) enters the heat exchanger (commonly plate or tube type). The flue gas exchanges heat with low-temperature waste gas to be treated (or other media needing heating, such as workshop fresh air or hot water), reducing its own temperature to 200~300°C.
4. **Purified Emission**:
The low-temperature flue gas after heat recovery is discharged through a chimney in compliance with standards. Meanwhile, the heated low-temperature waste gas (temperature can be raised to 300~500°C) re-enters the combustion chamber, reducing auxiliary fuel consumption and lowering operating costs.
B. Core Characteristics of TNV (Compared with RTO)
The structure and principle of TNV determine its obvious differences from RTO (Regenerative), with the following key characteristic comparisons:
| Comparison Dimension | Direct-Fired Thermal Recovery Incinerator (TNV) | Regenerative Incinerator (RTO) |
|---|---|---|
| Core Components | Combustion Chamber + Heat Exchanger (no heat storage medium) | Combustion Chamber + Heat Storage Chamber (ceramic heat storage medium) |
| Thermal Efficiency | Lower, typically 50%~70% | Extremely high, up to over 95% |
| Startup Speed | Fast, no need to preheat the heat storage medium; startup takes about 30~60 minutes | Slow, requires preheating the heat storage medium; startup takes about 2~4 hours |
| Suitable Concentration | Suitable for medium-to-high concentration VOCs (≥2000mg/m³); large amount of auxiliary combustion needed if concentration is too low | Suitable for low, medium, and high concentrations; still energy-saving via heat storage medium when concentration is low |
| Structural Complexity | Simple, low maintenance cost | Complex, requires regular maintenance of heat storage medium and switching valves |
C. Typical Application Scenarios
Due to its simple structure and fast startup, TNV is more suitable for the following scenarios:
- Treatment of medium-to-high concentration VOCs waste gas in the coating industry, such as solvent-based paint spraying in furniture factories and drying lines of automotive parts.
- Enterprises with intermittent production, which do not require long preheating and can start and stop quickly.
- Scenarios with clear waste heat requirements, such as factories needing to heat workshop air or produce hot water, which can directly utilize the heat recovered by the heat exchanger.
Treatment of TNV Waste Gas and Energy Recovery
TNV-Heat Recovery Type Waste Gas Incinerator
- TNV is particularly suitable for organic gases containing high-concentration VOCs.
- The combustion temperature can reach 780℃, effectively treating VOCs-containing organic waste gas through high-temperature cracking, with a treatment efficiency of up to 99.9%.
- The waste heat from combustion can be directly used in the drying process of automated production lines in the automotive or other industries.
- With further waste heat recovery, the final exhaust emission temperature can be reduced to below 120℃.
🔧Production Introduction
Direct Combustion Heat Recovery Waste Gas Incinerator (referred to as TNV)
The emergence of TNV has almost met the needs of waste gas treatment in all industrial production. With excellent product quality and high-efficiency systems, TNV can handle organic waste gases of various compositions.
Connecting heating combustion systems with thermal energy recycling equipment can significantly reduce energy consumption.
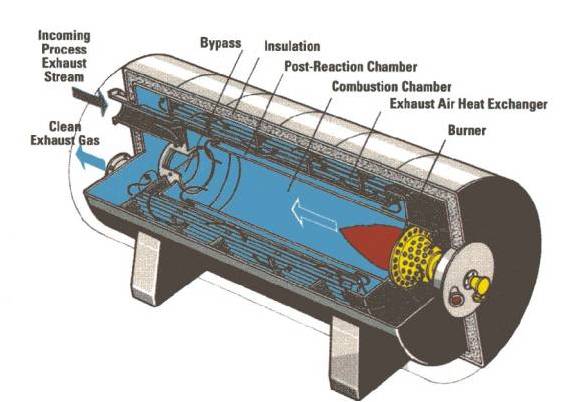
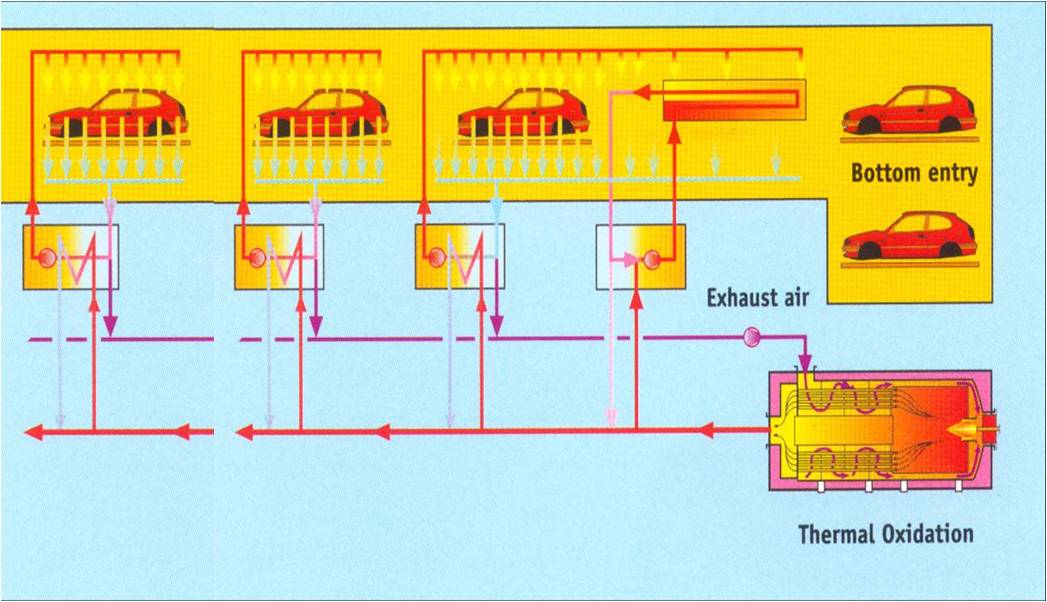
Processing Objects : malodorous waste air, VOCs gas (coating spraying gas, coating waste air, etc). Processing Capacity 3,000~60,000Nm³/h Removal Efficiency : it can be 99.9% Application: automobile industry (production line painting oven waste air incineration and heating system, spraying production line VOCs concentration plus incineration system), printing coating, color steel plate coating, chemical plant, pharmaceutical factory, etc. Brief Introduction: TNV (The Thermal Recuperative Oxidizer) is a high efficiency waste air abatement equipment whose clean gas outlet can supply a series of afterheat recovery devices. Features as follow: The temperature in the combustion chamber is 750 degree C and the waste air residence time is more than or equal to 1 second, which ensures the sufficient oxidation cracking. The outlet clean gas temperature is 400~570 degree C and one TNV can supply multiple heat exchangers (one TNV supplying seven heat exchangers is successfully applied in FAW Haima project). It is usually for paint shop oven heating system, spraying production line VOCs concentration incineration, desorption air heating system and other heating systems in automobile industry. Through the tubes integrated in the TNV, the waste air temperature can be above 400 degree C before it enters the combustion chamber. It greatly reduces the heat demand of burning and is more energy-efficient. Processing concentration range: 500mg/m³ -11g/m³ (less than 25% of the LEL lower limit).
🔧TNV (Thermal Oxidizer) + Heating System Application Cases
 FAW Haima Automobile Plant Project
FAW Haima Automobile Plant Project
 Geely Baoji Passenger Vehicle Project
Geely Baoji Passenger Vehicle Project
 Shaanxi Automobile Commercial Vehicle
Shaanxi Automobile Commercial Vehicle

Shaanxi Automobile Commercial Vehicle

